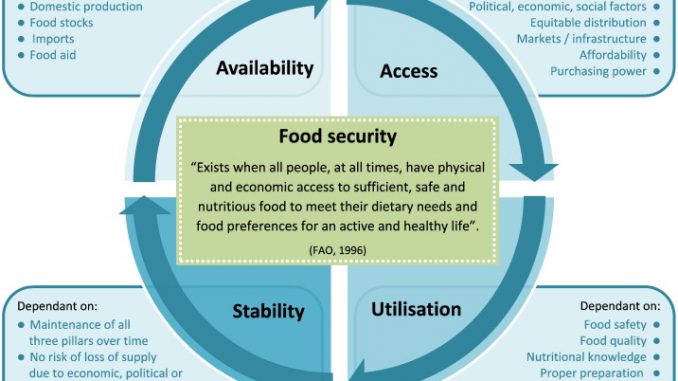
What is Food Security?
- Food security “exists when all people, at all times, have physical, social and economic access to sufficient safe and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.” – FAO, 1996
- The core concept of food security carries the access to healthy food and optimal nutrition for all.
- Household food security is the application of this concept to the family level, with individuals within households as the focus of concern.
- Food insecurity refers to a lack of access to enough good, healthy, and culturally appropriate food.

Characteristics of being Food Secured:
Concept of food security also includes the presence of following characteristics:
- Enough food: If there is adequate food as per one’s need and requirements.
- Good food: It should be with desirable taste, texture and other attributes.
- Healthy food: It should be nutritious and sustaining with proper vitamins, minerals, fibre, energy, and all the other things that our bodies need.
- Culturally appropriate food: Having access to culturally appropriate food means that people have food that they are familiar and comfortable with including availability of familiar foods & varieties.
Pillars of Food security:
Basically, there are four pillars/components of food Security. They are:
- Food availability:
- Having sufficient quantity of appropriate food available.
- It includes: domestic production, import capacity, food stocks, food aid.
- Accessibility:
- Physical and economic access to food
- Purchasing power, income of population, transport and market infrastructure
- Utilization:
- It includes adequate dietary intake and ability to use nutrients in the body.
- Food safety, hygiene and manufacturing practices applied in primary agricultural production, harvesting and storage; food processing; transportation, retail, households, diet quality and diversity: meeting needs in terms of energy, macro- and micronutrients.
- Stability:
- Stability of supply and access
- Weather variability, price fluctuations, political factors, economic factors

Dimensions of food security and its determinants:
| Availability | Accessibility | Utilization | Stability |
| · Domestic production
· Import capacity · Food stocks · Food aid |
· Income, purchasing power, own production
· Transport and market infrastructure · Food distribution |
· Food safety and quality
· Clean water · Health and sanitation · Care, feeding and health seeking practices |
· Weather variability, seasonality
· Price fluctuations · Political factors · Economic factors |
- Source: FAO
Factors affecting Food Security:
The food security can be mainly influenced by:
- Low per capita income
- Low and unequal distribution of income
- Poor and highly unstable growth performance especially in agriculture
- Unemployment and underemployment
- Low and declining farm size
- Inequalities in land distribution
- Low land utilization
- Social discrimination
- Population growth
- Access to market
- Food taboos: certain restrictions in the food consumption due to cultural and social norms.
- Poverty
- Climate induced insecurity: climate change, deforestation, landslide, declining soil fertility
- Political instability
- Poor, marginalized, ethnic group & lower caste groups
- High maternal and infant mortalities
Urbanization Affecting Food Security?
Urbanization is a process whereby populations move from rural to urban area, enabling cities and towns to grow. It can also be termed as the progressive increase of the number of people living in towns and cities.

Urbanization is influencing the dimensions of the food security as:
- Availability:
- There is an effect on the food supply which may run insufficient due to competition between areas used for agricultural production and areas used for expanding urban settlements.
- The food demand may vary between the rural and urban food with decrement in the availability of staple foods.
- Accessibility:
- The high prices may put up a restriction into consumption of the desired food needs.
- There is need to rely partly upon commercial food value earners like street vendors, small merchants, etc who have increased number.
- Utilization:
- Lack of regulations in the urban setting for street stands and commercial workers impact upon low food security.
- The urban food consumption has a transition of malnutrition from under nutrition to over nutrition, giving rise to obesity, hypertensions, etc.
- Stability:
- The fluctuating prices of certain foods due to the changes in demand of urban populations create a barrier to people in food consumption.
- The political conflicts may arise due to clash of thoughts among huge population which may be a cause to overlook food security.
- The risk of increasing food insecurity I higher in slums and informal settlements where, in many cases, socio-economic development is already lower than in rural areas
Food Security Affecting Urbanization?
The food security is also having an influence in urbanization as:
- Food insecurity among the commercial workers has led to overcrowding of this population group.
- Urban poverty (increment of slum areas in urban setting) has increased due to lack of access to food.
- The management of the urban areas is decreasing due to lack of human resource that are food secured.
- Gap between the rich and poor is in increasing trend due to issues of food security.
- The constant existence of political conflicts arises due to demand of food security among minority population.
- Increased food insecurity has led to criminal activities including theft, robbery, etc. which are more prevalent in the urban areas
- Lack of food has created a barrier among the civil society and government causing lack of co-ordination for urban management.
References and for more information:
http://www.fao.org/docrep/005/y4671e/y4671e06.htm
http://www.ifpri.org/topic/food-security
https://sites.google.com/site/indiaswaterfoodsecruity/home/three-pillars-of-food-security
https://wocatpedia.net/wiki/Definition_and_Dimensions_of_Food_Security
http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/ERP/uni/FIMI.pdf
https://www.unicef.org/albania/Food_Security_ANG.pdf
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/01/food-security-and-why-it-matters/
https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/196772/2/Mannaf%20and%20Taj%20Uddin.pdf
https://www.wfp.org/climate-change/climate-impacts
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22002569
http://www.masterhdfs.org/masterHDFS/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/4-FS-CI-Ad..pdf
http://www.fsincop.net/fileadmin/user_upload/fsin/docs/resources/167.full.pdf
http://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/109/31/12315.full.pdf
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-four-dimensions-of-food-security_fig1_51111347
http://www.fao.org/docrep/013/al936e/al936e00.pdf
http://www.fao.org/elearning/course/fa/en/pdf/p-01_rg_concept.pdf
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jsfa.4666
http://www.fao.org/docrep/w0078e/w0078e04.htm
https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/81593
http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1138191/FULLTEXT01.pdf
https://www.slideshare.net/MahmudShuvo2/urbanization-and-its-effect-on-food-security
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-43739-2_32
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2935117/
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/263590485_Urbanization_and_Food_Security
http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/user_upload/esag/docs/RapidUrbanizationFoodSecurity.pdf
https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/urbanization.htm
https://www.slideshare.net/shahkhushbu/urban-poverty-65045617
https://www.ukessays.com/essays/geography/urban-poverty.php
https://www.slideshare.net/dvanecoutinho/food-security-60089125
https://www.slideshare.net/AllahDadKhan/four-pillars-of-food-security-a-lecture-by-mr-allah-dad-khan
https://www.slideshare.net/JulietAbisha/food-security-69788069
https://www.unicef.org/albania/Food_Security_ANG.pdf
http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/faoitaly/documents/pdf/pdf_Food_Security_Cocept_Note.pdf
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13600818.2015.1067292
https://foodforward.org/2017/10/what-is-food-insecurity/
https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-food-insecurity-definition-impact-prevention-efforts.html