Table of Contents
What Is Population Growth?
- Population is defined as a cluster of individuals or same kind of species or group of societies living in an exact habitation or environment at the same period.
- Population is a specific group of individuals or a pool of individuals.
- A population may change or escalate and decline due to fluctuation in birth rate, death rate, emigration and immigration.
- Population growth simply means the increase in size of the population.
- Population growth is the alteration/increase in a population above time.
- Population growth can be calculated as the alteration in a number of individuals of any species in a population using “per unit time” for measurement.
- Population growth is measured equally in absolute and relative terms.
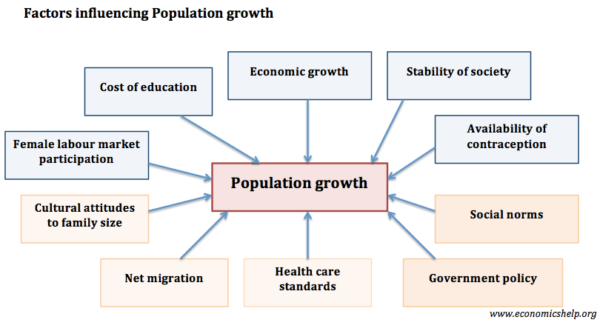
What are the Major Factors affecting Population Growth?
Population growth is based on four fundamental factors: birth rate, death rate, immigration and emigration.
Population growth rate= (birth rate + immigration) – (death rate + emigration)
1. Birth Rate:
- The population logically escalates if the number of births is more than the number of deaths at any particular time or if the death rate is less or slower in respect to the birth rate.
- The formula for calculating crude birth rate is:
Crude Birth Rate (CBR) = (Number of births within a year/Total mid-year population) × 1000
2. Mortality Rate/Death Rate:
- A crucial reason affecting the growth of the population is the death, or mortality rate.
- As the birth of new individuals escalates the population size, deaths decline it. The issues that affect the mortality rate consist of the accessibility and affordability of quality health care and daily life practices.
- The formula for calculating Crude Death Rate is:
Crude Death Rate (CDR) = (Number of deaths within a year/Total mid-year population)× 1000
3. Immigration and Emigration:
- Migration is the transferring of people from one place/country to a different place/country.
- There are two types of migration; Immigration and Emigration.
- Immigration (moving Into the place/country) is the movement of individuals into a population from other areas.
- Emigration (Exiting from a place/country) is the movement of individuals out of a population.
- Both Immigration and Emigration affects the population size of desired nations.
- A number of factors, such as running away from war, searching and finding good education, pursuing a career, searching new jobs or union with family members, results in emigration.
- When an individual emigrates from a nation, its population declines gradually.
- When somebody travels to a country from another place, it is known as immigration (into the country).
- There are pull and push factors of migration.
- Pull factors attract people towards a certain place/country. Example of pull factors include; better job opportunities, social securities, better health facilities and improved education systems etc.
- Push factors force people to leave the place/country. Examples of push factors include; lack of social harmony and peace, increased conflict, war, poor education systems, poor job opportunities, lack of adequate resources etc.
Other Factors that Affect Population Growth:
a) Government Plans/Policies:
- Government plans and policies have a significant effect on population growth.
- Some people around the world, including legislators, administrators are certain that some countries prerequisite is to have a birth rate restriction.
- In fact, China already had its widely known one-child policy where it restricted couples from being able to have more than the limited number of children. Therefore, this dispute supports that this type of restriction would cause fewer resources utilization and avoid overpopulation.
- Moreover, different countries and governments have brought different plans and policies to control population growth.
b) Biotic and intrinsic factors:
Biotic and intrinsic factors include:
- Age of reproductive maturity
- Number of offspring produced per reproductive event
- Number of reproductive events in a lifetime.
These three factors are together known as fecundity.
c) Environmental factors:
- Environmental resistance factors
- Carrying capacity
d) Emancipation/liberation of women:
- Increasing emancipation/liberation/freedom of women have increased their access to education, work and other outdoor activities, ultimately leading to delayed child bearing.
- It also results in fewer children being born per women.
e) Urbanization:
- Urbanization leads to increased birth rates and decreased death rates.
- Birth rate increases because people have more access and utilization of medical facilities in the urban areas. As a result, neonatal and infant mortality also decreases.
- However, it should be remembered that birth rate might also decrease in urban areas due to more education/awareness among the people and increased use of family planning devices.
f) Agricultural changes:
- Agricultural changes have increased production of foods.
- Increased production of foods has decreased deaths due to famine.
- Additionally, regular supply of foods has increased/promoted birth rates as people can ensure that they can feed their children.
g) Education:
- Education is an important factor of population growth.
- Increase in education level increases use of family planning devices, increased planning of resources etc., thus leading to decreased birth rates.
- Additionally, education sensitizes people of basic WASH (Water, Sanitation and Hygiene) measures which prevents people from simple and preventable life-taking diseases like diarrhea, cholera, typhoid etc.
Consequences of Population Growth
- Rapid population expansion has significant economic implications.
- It promotes income inequity; it holds down the pace of expansion of the gross national product by limiting savings and capital investments; it puts pressure on agricultural production and land; and it causes unemployment.
- Furthermore, the quality of education for an expanding number of children is harmed, as large proportions of children reduce the amount of money available for each child’s education from the educational budget; similarly, the cost and adequacy of health and welfare services are harmed.
- Maternal death and disease, as well as physical and mental retardation in children from low-income families, are all major repercussions of rapid population expansion.
- Population expansion, on the other hand, has a favorable impact on societies.
- Economic gains like as tax base expansion and higher consumer spending at local firms are among them, as are benefits resulting from cultural changes aimed at keeping up with rising populations.
Factors Affecting Fertility, Mortality and Migration:
Factors Affecting Fertility:
1. Biological Factors
- Sex and Age, mensuration
2. Physiological factors
- Sterility- phases in the reproductive pattern of a woman when she is not able to conceive and is sterile.
3. Social factors
- Religion
- Caste system
- Racial groups
- Customs
- Family systems
- Education
- Status of women
4. Economic factors
- Urbanization
- Occupation
- Economic Conditions
- Family planning
Factors affecting Mortality:
1. Disease control medicines
- International collaboration and support from developed countries has helped developing countries in the provision of importing drugs from technologically advanced countries.
- Therefore, the provision has been helpful in eradicating particular diseases like malaria, smallpox, polio, TB, etc. to a substantial level.
2. Public Health Programs
- Developing countries with the aid of WHO are launching various public health programmes like free immunization campaigns, environment conservation, tobacco control programs.
- Likewise, government has made different provisions on pollution control measures. As a result, deaths due to respiratory diseases have also declined.
3. Medical facilities
- Various medical, health care facilities establishment from the past years has played an important role in combating infectious diseases.
- Increment of government and private hospitals in a meteoric phase are providing best medical facilities, which certainly helps in declining death rates.
4. Increased Education
- Education on healthy lifestyle, healthy habits, and a balanced diet have made people health conscious which certainly helps in decline death rates through health education.
5. Status of Women
- The spread of literacy in most of the developing countries has made women empowered and have understood the importance of sanitation and hygiene, in result; they take better care of their children. Likewise, the infant mortality rate declines.
6. Food supply
- By the means of a rise in the food supply in the mainstream of developing countries and through imports of food grains from developed countries. Famines are controlled which has led to the reduction of death rates in such nations.
7. Life Expectancy
- Through economic development i.e. rise in per capita incomes, improved health facilities, etc. in developing countries; it has been able to increase the life expectancy rate of the people compared to past years, which consequently decline the death rate.
Factors affecting Migration
1. Socio-political factors
- Various political reasons, political disputes and arguments lead to war and increased level of conflict. In result, it is the major factor affecting migration.
- Example: In Syria, people migrated from one country to another for security and access to health care.
2. Economic factors
- Factors like the unemployment situation, brain drain, decline phase of business come under economic factors.
- Additionally, higher wages, higher and better job opportunities etc. lead to migration of skilled labors/intellectuals to developed areas/countries.
- Therefore, such reasons are responsible for the factors affecting migration.
3. Ecological factors
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report put forward that climate change would have its major effect upon food security by the middle of this century.
- Areas that can no longer put up with agriculture will possibly experience rural to urban migration or bigger intensities of international emigration.
- An additional factor that can result in severe food insecurity is water security. Growing water insecurity in different parts of the globe has the possibility to affect international migration.
- Individuals who are brutally obstructed by altering ecological conditions may select to migrate from their native country in search of more eco-friendly surroundings in a different place.
References And For More Information:
http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/population-growth.html
https://serc.carleton.edu/quantskills/methods/quantlit/popgrowth.html
https://enviroliteracy.org/environment-society/population-studies/basic-population-concepts/
https://www.life.illinois.edu/bio100/lectures/s10lects/04s10-population.html
https://sciencing.com/calculate-per-capita-7505706.html
https://www.watt-watchers.com/activity/population-math/
http://www.sociologydiscussion.com/demography/5-main-factors-affecting-the-fertility-in-women/2956
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12340809
https://bizfluent.com/info-8252744-factors-affect-growth-population.html