
Table of Contents
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the term used to describe the development of computer systems that are capable of carrying out tasks that would typically require human intelligence.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intellectual functions by technology, particularly computer systems.
- Healthcare, banking, transportation, and entertainment are just a few of the many domains where AI has applicability.
What does Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Health Care Mean?
- The use of machine learning (ML) algorithms and other cognitive technologies in healthcare is referred to as artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare.
- AI in healthcare is used to quickly examine enormous amounts of clinical documentation assists in the identification of disease signs and trends.
- Healthcare and artificial intelligence (AI) have a wide range of possible uses, from analyzing radiological images for early detection to forecasting outcomes from electronic health information.
How is Artificial Intelligence (AI) Used in Health Care?
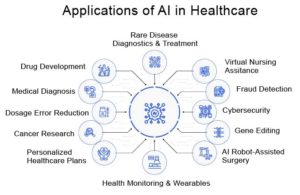
Medical imaging
- AI algorithms can analyze medical images, such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, to detect and diagnose diseases with greater accuracy and speed than human radiologists.
Electronic health records
- AI can analyze electronic health records (EHRs) to identify patterns and trends in patient data, helping clinicians make more informed decisions about diagnosis and treatment.
Drug discovery
- AI can help researchers identify potential new drugs by analyzing large datasets of molecular and clinical data.
Personalized medicine
- Utilizing a patient’s particular genetic, environmental, and behavioral characteristics, AI can assist clinicians in customizing treatment approaches for individual patients.
Virtual assistants
- AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide patients with personalized health advice and support, improving patient engagement and satisfaction.
Predictive analytics
- AI can analyze patient data to predict the likelihood of adverse health events, such as hospital readmissions, and enable clinicians to intervene early and prevent such events from occurring.
Robot-assisted surgery
- AI can help guide surgical robots to perform minimally invasive procedures with greater precision and accuracy.
Importance of AI in health care
More accurate diagnosis
- AI algorithms can analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, with greater accuracy and speed than human radiologists.
- This can lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses, improving patient outcomes.
Improved efficiency
- AI can automate routine tasks, such as appointment scheduling and medication refills, freeing up healthcare providers to focus on more complex tasks, such as patient care.
- This can improve efficiency and reduce healthcare costs.
Predictive analytics
- AI can analyze patient data to predict the likelihood of adverse health events, such as hospital readmissions, and enable clinicians to intervene early and prevent such events from occurring.
- This can improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Drug discovery
- AI can help researchers identify potential new drugs by analyzing large datasets of molecular and clinical data.
- This can speed up the drug discovery process and improve treatment options for patients.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Improved diagnostic process effectiveness
- Cost-Efficient and Resourceful
- Real-Time Access to Information
- Safer procedures
- Improved medical treatment
- Simple information exchange
- Improved preventative care
Limitations
Needs Human Supervision
- Running them will still require human monitoring and surveillance because AI is not flawless.
- Robotic systems, such as those used in surgical procedures, lack empathy and only follow instructions.
Construct social biases
- Healthcare AI relies on algorithms that may find it handy for most people (i.e. nearest possible clinic or hospital for a patient).
- Nevertheless, this does not consider a patient’s financial status or if they feel comfortable visiting the facility that was suggested by AI.
Replacing human workers
- As previously noted, there is a danger that certain staff within the healthcare may no longer be required as their positions may be replaced by AI because AI can handle the majority of the menial and repetitive human labor in healthcare.
Potential Security Threats
- The most glaring and direct drawback of AI in healthcare is the potential for data privacy security breaches.
Low Interpretability
- Due of the complexity of AI systems, it can be challenging for healthcare practitioners to comprehend how they came to their conclusions.
Expense
- The development and implementation of AI systems can be expensive, which may prevent their widespread use in healthcare.
Examples of AI in Health Care
PathAI
- PathAI provides healthcare professionals with advanced Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence tools to improve the accuracy of cancer diagnosis.
- By minimizing errors in the diagnostic process and offering innovative techniques for individualized medical treatment, PathAI helps pathologists make more precise diagnoses.
Early diagnosis of fatal disease
- Artificial Intelligence technology has been particularly useful in the early detection of potentially deadly blood-related diseases.
- With the aid of AI-enhanced microscopes, doctors can quickly scan blood samples for harmful substances and bacteria, including Staphylococcus and E. coli, reducing the time it takes to detect these diseases.
Customer service chatbots
- Customer service chatbots, developed using Natural Language Processing (NLP) technology, enable patients to raise their concerns and questions about appointments, bill payments, and other matters.
Ethical Issues in the Use of AI in Health Care
Bias and Discrimination
- AI systems are trained on data, and if the data used to train them is biased, the AI systems can perpetuate and even amplify existing biases in healthcare.
Data Privacy and Security
- AI systems in healthcare often require access to sensitive patient data, which raises concerns about data privacy and security.
Autonomy and Informed Consent
- AI systems may collect and analyze patient data without explicit consent, and patients may not fully understand how their data is being used or have the opportunity to exercise autonomy over the use of their data.
Equity and Access
- AI systems in healthcare may exacerbate existing disparities in access to healthcare services.
Social Gaps and Justice
- The issue of social gaps is another issue that poses a threat to society as a result of the development of AI.
- Every advancement, discovery, and invention increases social inequality and reduces social fairness for people everywhere in the world.
Future of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Health Care
- In the future of healthcare, artificial intelligence is anticipated to be crucial, notably in precision medicine and image analysis.
- The biggest challenge is making sure that it is adopted in routine clinical practice.
- It is anticipated that AI will support human clinicians rather than replace them.
- Within five years, there should be a limited application of AI in clinical practice, and within ten years, a more widespread use.
- Only healthcare professionals who refuse to collaborate with AI run the risk of losing their careers.
References and For More Information
https://bmcmedinformdecismak.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12911-021-01488-9
https://neoteric.eu/blog/benefits-of-ai-in-healthcare/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6616181/
https://www.techtarget.com/searchenterpriseai/definition/AI-Artificial-Intelligence
https://www.foreseemed.com/artificial-intelligence-in-healthcare
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8382232/
https://intellipaat.com/blog/artificial-intelligence-in-healthcare/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8826344/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6616181/