Table of Contents
What is Asthma?
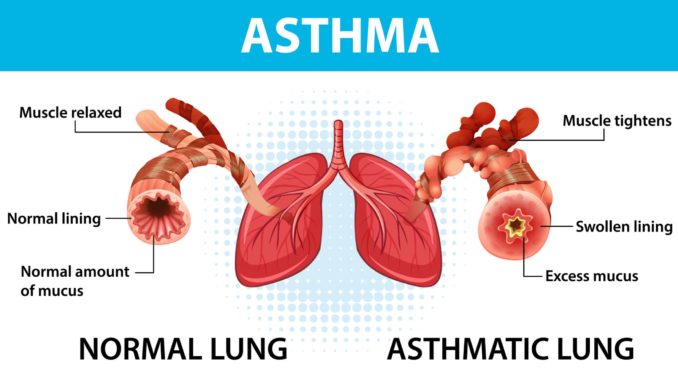
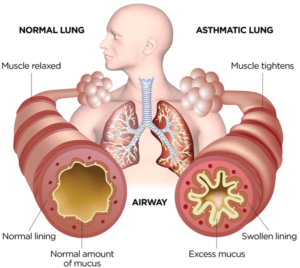
- Asthma is a common lung disease that leads to short-term breathing difficulties.
- Asthma is a chronic lung condition that involves inflammation in the airways of the lungs.
- This inflammation causes the airways to become restricted due to stiffness in the surrounding muscles and makes the person difficult to breathe.
- Asthma causes the airways to constrict, swell, and occasionally generate more mucus.
- It is characterized by inflammation of the airways, which can cause breathing difficulties, chest tightness, wheezing, and coughing.
- Besides making it hard to breathe, asthmic condition can also hinder the performance of certain physical activities, rendering them arduous or impractical.
Key Facts
- Asthma is a chronic condition that requires long-term management and is one of the most common non-communicable diseases.
- Throughout all age categories, asthma prevalence and burden have been steadily rising internationally, making it a critical public health issue.
- It is a major concern on a global scale and the most significant disorder in terms of the severity and duration of disability.
- The year 2019 saw 455,000 deaths caused by asthma while an approximate of 262 million individuals worldwide were affected by the condition.
- Asthma-related deaths are more prevalent in low- and lower-middle-income nations where there is a lack of diagnosis and proper treatment.
- The prevalence of asthma varies from country to country and is more common in developed nations.
- Asthma is not contagious, but it can be hereditary.
- There is no cure for this condition, but it can be controlled with proper management and treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Asthma is caused by both genetic and environmental factors.
- It is more likely to occur in individuals who have a family history of asthma, particularly if a close relative such as a parent or sibling is affected.
- People who have other allergic conditions, like eczema and hay fever, are also at greater risk of developing asthma.
- Urbanization is linked to higher rates of asthma.
- Early-life events, including exposure to air pollution, tobacco smoke, and viral infections, as well as low birth weight and prematurity, can influence lung development and increase the likelihood of the disease.
- Exposure to various environmental irritants and allergens, such as indoor and outdoor pollution, dust mites, molds, and occupational chemicals, fumes, or dust, can also raise the risk of asthma.
- Both children and adults who are overweight or obese face a greater risk of asthmic condition.
- Other risk factors include respiratory infections, exercise, and emotional stress.
Source: https://www.childrensrespiratorydoctor.co.uk/blog/can-asthma-cured-forever/
Symptoms of Asthma
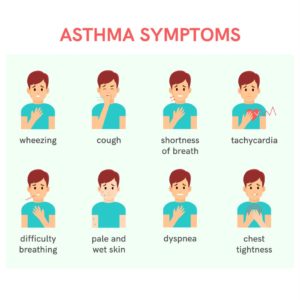
- Symptoms can vary from person to person and may range from mild to severe.
- Its symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing, mainly while exhaling and sometimes when inhaling
- Coughing
- Chest tightness
- Symptoms may be triggered by exercise, allergens, irritants, respiratory infections, and changes in weather.
Diagnosis of Asthma
- To diagnose asthma, a thorough medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests are necessary.
- Doctors may also use imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans to rule out other conditions.
- Allergy testing may also be recommended to identify potential triggers.
Emergency Situations
- Severe asthma symptoms can sometimes progress to a life-threatening emergency, with signs including rapid breathing, bluish lips or face, severe chest pain, and difficulty speaking or walking.
- Seeking immediate medical attention is critical in cases of asthma, particularly in instances where symptoms are severe.
- Other signs of severe asthma include persistent wheezing or shortness of breath, especially at night or in the morning, being unable to speak more than a few words due to shortness of breath, and having to use chest muscles to breathe.
- Inaccurate readings from peak flow meters and no improvement after taking a quick-acting inhaler are also warning signs.
Complications of Asthma
- Untreated or poorly managed asthma can result in various complications, including respiratory failure, pneumonia, and bronchitis.
- This can also heighten the likelihood of developing other respiratory ailments such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- In addition, asthma symptoms that impede with sleep, work, and other activities, may lead to sick days from school or work.
- Over time, untreated asthma can cause permanent narrowing of the bronchial tubes, which can negatively impact breathing.
- Severe asthma attacks may result in emergency room visits and hospitalizations.
- Moreover, some medications used to stabilize severe asthmic conditions can cause side effects when used over an extended period.
Prevention
- While there is no known cure for asthma, it is possible to prevent or reduce symptoms by avoiding triggers such as smoke, air pollution, and allergens.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a nutritious diet, can also help improve lung function.
Treatment
- Treatment for asthma typically involves long-term management with the use of inhalers, medications, and lifestyle changes.
- Inhalers, such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids, help relieve symptoms and reduce inflammation.
- In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to manage symptoms.
WHO Response on Asthma
- WHO acknowledges this disease as a part of its Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of NCDs and the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- WHO is addressing asthma diagnosis and treatment through its Package of Essential Non-communicable Disease Interventions (PEN), which includes protocols for chronic respiratory diseases like asthma.
- WHO is also working towards reducing tobacco smoke exposure through initiatives like MPOWER and mTobacco Cessation, and the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control.
- The Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases (GARD) is another voluntary alliance that contributes to WHO’s work to prevent and control chronic respiratory diseases.
References and For More Information
https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ854239.pdf
https://asthmarp.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40733-022-00087-3
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/asthma
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/asthma/
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/6424-asthma
https://www.cdc.gov/asthma/default.htm
https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ854239.pdf