- Before knowing about Project Management Cycle, let us know a brief about Project. Project is the sequence of task to achieve the pre-set goal and objectives in a given time frame.
- According to Business Dictionary, Project is “A planned set of interrelated tasks to be executed over a fixed period and within certain cost and other limitations.”
- Project is temporary and unique.
- Project management then refers to the application of knowledge skills, and tools to achieve the project goals and complete them in time.
Table of Contents
What is Project Management Cycle?
- Project management cycle (PMC) is the process of planning, organizing, coordinating, and controlling of project effectively and efficiently from start to the end in order to achieve pre-defined objectives.
- Project management cycle involves the series of activities that is followed through stages of project completion to achieve its goal.
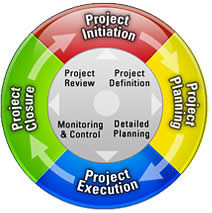
Phases of Project Management Cycle (PMC):
- In general, Project Management Cycle consists of four major phases. However, some methodology also uses the fifth phase, known as monitoring. Here, we have included this fifth phase under the execution and closure.
- Four phases of PMC are:
-
Initiation Phase
-
Planning Phase
-
Execution Phase
-
Closure/Termination Phase

1. Initiation Phase:
- This is the beginning phase of the project.
- Project has not been formed yet.
- This is the phase where literature review and secondary data analysis is done.
- It includes information such as:
- Purpose, vision and mission of the project
- High level project description
- Summary milestones of the project
- Here, the idea of project is seeded.
- The problem is identified and checked if the project can solve it.
- Basically, the feasibility of the project is assessed and identified.
- Things to complete during this phase include:
- Undertaking the feasibility study of the study
- Assessing the scope of work of the project
- Identifying the deliverables
- Identifying stakeholders of the project
- Comparing the potential costs and benefits of the project
2. Planning Phase:
- Planning phase is an important phase of project. The better the plan, easier will be the execution.
- Planning phase begin after the project in the initial phase gets confirmation to launch
- In this phase, we need to break down larger activities into smaller tasks.
- It is the phase where the plans for conducting the project are formed in detail.
- Project planning involves two parts:
- Strategic Planning: Here, we develop overall approach to the project
- Implementation Planning: Here, we figure out the details of how the project will be implemented
- SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Timebound) goals and objectives are set.
- It includes planning of resources, risk, finances etc.
- Roles and responsibilities of the staffs are clearly defined
- At the end of this phase, the plan is documented for the future purpose.
- Things to complete during this phase include:
- Project plan
- Resource (3M- Money, Manpower and Materials) plan
- Budget and financial plan
- Quality plan
- Risk plan (Anticipating the risks)
- Acceptance plan
- Communication plan
- Procurement plan
3. Execution Phase:
- Project execution is the phase where plan is now brought into action, after the final approval and completion of all planning.
- This is very intimidating phase of project where we can see the actual work happening.
- A series of activities is carried out to meet the goals.
- Earlier drafted plan acts as the guide to all the action.
- Monitoring of the work goes side by side during execution. Monitoring is done to ensure that the activities are moving on track, as planned. Moreover, it will also involve immediate rectification and changes required to meet the overall goal and objective of the project
- This phase also involves mid-term evaluation of the project.
- Steps for project execution phase includes:
- Creating tasks and organizing workflow
- Provide necessary guidance, briefing and trainings to the team members
- Regular communication with the team members
- Monitoring the quality of work
- Managing budget
- Things to ensure during this phase include:
- Time management
- Cost management
- Quality management
- Change management
- Risk management
- Issue management etc.
4. Termination Phase:
- This phase is also known as the closure step or closure phase.
- As the project is temporary it has to come to an end
- By this time all the activities have been carried out
- The contractors hired, staffs of the project are terminated
- At the end evaluation report is created that would evaluate the overall success of the project and are useful for future reference as well.
- Things to ensure during this phase include:
- Analysis of project performance regarding its goals and objectives
- Analysis of team performance
- Documentation of project closure
- Conducting a final analysis of the project
- Closing the finances and budgetary aspects of the project

Characteristics of a Project Management Cycle:
Irrespective of the size and modality of the project, all projects/project management cycle must have following characteristics:
a) Consistency:
- No matter what project you are doing consistency needs to be maintained.
- There are the certain standards that are to be met during project cycle.
- Consistency at all stages of PMC helps in maintaining the quality of the project.
- Consistency regarding success standards are also important.
b) Flexibility:
- Project has to be consistent but it doesn’t mean that PMC is rigid.
- PMC needs to be amended depending upon the nature of the project.
- To acknowledge the project and its peculiarity, PMC is flexible.
c) Transparency:
- It is the most important feature of the project.
- All works at all stages of PMC needs to be transparent
- Transparency needs to be maintained especially at the time of resource planning
- Transparency would help in avoiding the conflict in the project.
Advantages of the PMC:
1. Goal achievement
- The main objective is to achieve the goal of project and the whole PMC works to achieve
- The plan, execution all helps to meet the goals in give time frame.
- Also, the goals are made SMART
2. Effective use of time and resources
- The PMC helps in optimum utilization of resources and time
- The resource plan done at the beginning helps in effective utilization
3. Better Communication
- All the staffs come together in planning and brain storming the ideas which fosters the better communication
- Pre-identified roles and responsibilities helps to avoid the unwanted tension
- Project is the team work and performed as one
4. Risk assessment
- One of the major features of the PMC is risk assessment.
- It is done at the planning phase.
- Risk when assessed earlier and staying prepared helps to tackle them.
Disadvantages and Limitations of PMC:
1. High cost
- With already limit in project budget, conducting and ensuring the details of all sessions of the cycle can increase the cost.
2. Complex
- PMC can make the project look more complex, as there are many steps and activities to follow.
- Rigidity in plan, can create the stressful environment.
3. Lack of creativity
- PMC sometimes can suppress the creativity
- The deadlines, stressful environment pre-defined activities and procedure may not let the creativity of the staff to sprout out.
References and For More Information:
https://www.mavenlink.com/resources/what-is-the-professional-services-project-life-cycle
https://www.smartsheet.com/blog/demystifying-5-phases-project-management
https://www.lucidchart.com/blog/the-4-phases-of-the-project-management-life-cycle
https://www.clarizen.com/project-management-life-cycle/
https://bizfluent.com/info-8774906-describe-advantages-disadvantages-project-management.html
https://www.apm.org.uk/blog/the-benefits-of-following-a-project-management-method/
https://www.pmi.org/about/learn-about-pmi/what-is-project-management
https://www.ims-web.com/blog/key-characteristics-of-project-management-processes
https://ec.europa.eu/europeaid/aid-delivery-methods-project-cycle-management-guidelines-vol-1_en
http://www.method123.com/project-plan.php
https://www.project-management-skills.com/project-management-life-cycle.html