Table of Contents
What is Rule of Law?
- Rule of law, also known as supremacy law, means that no one (including government) is above the law, law is above everyone, and it applies to everybody.
- The term ‘rule of law’ is derived from the French word ‘le principe de legalite’ which means ‘the principle of legality’.
- The rule of law is a legal principle that law should govern a nation and not arbitrary decision by individual government officials.
- According to Black’s Law Dictionary, the rule of law, also known as “the supremacy of law”, provides that decisions should be made by the application of known principles or laws without the intervention of discretion in their application’.
- Rule of law is a process/practice that supports equality of all citizens before the law and prevents arbitrary use of power/authority.
- Rule of law is a set of principles, or ideals, for ensuring an orderly and just society.
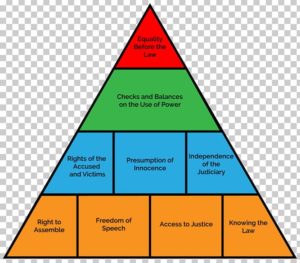
- There are three major elements of rule of law;
- Supremacy of the law
- Equality before the law
- Predominance of legal spirit: court should be free from impartiality and external influence.
- Rule of law ensures that fundamental rights are protected and justice is accessible to all.
- Rule of law is a principle of governance where all persons, institutions and entities are held accountable to the laws and regulations.
- Rule of law ensures that the law is equally enforced and independently decided for everyone.
- According to the Rule of Law, a law should be:
- open and clear
- general in form
- universal in application
- knowable to all
- The rule of law, in the purist sense, is an ideal, a goal, something to strived for.
- Rule of law is an integral element of humanitarian and human right agendas.
- Rule of law is one of the key dimensions that determine the quality and good governance of a country.
Principles of Rule of Law:
According to the World Justice Projects definition, rule of law is a system in which the following four principles are upheld. These are also known as the four universal principles of rule of law:
1. Accountability
- The government and its officials, its agents as well as individuals and private entities are accountable under the law.
2. Just law
- The laws are clear, publicized, stable and just; and are applied evenly; and protect fundamental rights including the security of the persons and property.
3. Open government
- The process by which the law is enacted, administered and enforced is accessible, fair and efficient.
4. Access and impartial justice
- Justice to be delivered timely by competent, ethical, and independent representatives and neutrals.
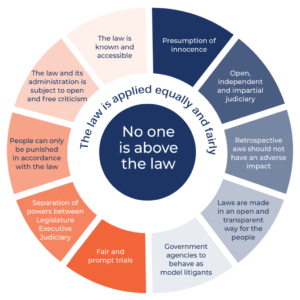
Additional Principles of Rule of Law
- No one is above the law
- Everyone is treated equally under the law
- Everyone is held accountable to the same laws
- There are clear and fair processes for enforcing laws
- There is an independent judiciary, and human rights are guaranteed for all.
Characteristics of Rule of Law
- Transparency
- Accountability
- Public participation in decision making
- Fairness/justice in the application of law
- Separation of power
- Independent and impartial judiciary
- Legal certainty
- Avoidance of randomness/unpredictability
- Predictable resolution of disputes
Factors of Rule of Law
According to the World Justice Project, there are 8 factors of rule of law. They are:
1. Constraints on Government Powers
Sub-factors:
1.1 Government powers are effectively limited by the legislature
1.2 Government powers are effectively limited by the judiciary
1.3 Government powers are effectively limited by independent auditing and review
1.4 Government officials are sanctioned for misconduct
1.5 Government powers are subject to non-governmental checks
1.6 Transition of power is subject to the law
2. Absence of Corruption
Sub-factors:
2.1 Government officials in the Executive Branch do not use public office for private gain
2.2 Government officials in the judicial branch do not use public office for private gain
2.3 Government officials in the police and the military do not use public office for private gain
2.4 Government officials in the legislative branch do not use public office for private gain
3. Open Government
Sub-factors:
3.1 Publicized laws and government date
3.2 Right to information
3.3 Civic participation
3.4 Complaint mechanisms
4. Fundamental Rights
Sub-factors:
4.1 Equal treatment and absence of discrimination
4.2 The right to life and security of the person is effectively guaranteed
4.3 Due process of law and rights of the accused
4.4 Freedom of opinion and expression is effectively guaranteed
4.5 Freedom of belief and religion is effectively guaranteed
4.6 Freedom from arbitrary interference with privacy is effectively guaranteed
4.7 Freedom of assembly and association is effectively guaranteed
4.8 Fundamental labor rights are effectively guaranteed
5. Order and Security
Sub-factors:
5.1 Crime is effectively controlled
5.2 Civil conflict is effectively limited
5.3 People do not resort to violence to redress personal grievances
6. Regulatory Enforcement
Sub-factors:
6.1 Government regulations are effectively enforced
6.2 Government regulations are applied and enforced without improper influence
6.3 Administrative proceedings are conducted without unreasonable delay
6.4 Due process is respected in administrative proceedings
6.5 The Government does not expropriate without lawful process and adequate compensation
7. Civil Justice
Sub-factors:
7.1 People can access and afford civil justice
7.2 Civil justice is free of discrimination
7.3 Civil justice is free of corruption
7.4 Civil justice is free of improper government influence
7.5 Civil justice is not subject to unreasonable delay
7.6 Civil justice is effectively enforced
7.7 Alternative Dispute and Resolution Mechanisms are accessible, impartial, and effective
8. Criminal Justice
Sub-factors:
8.1 Criminal investigation system is effective
8.2 Criminal adjudication system is timely and effective
8.3 Correctional system is effective in reducing criminal behavior
8.4 Criminal system is impartial
8.5 Criminal system is free of corruption
8.6 Criminal system is free of improper government influence
8.7 Due process of the law and rights of the accused
9. Informal justice:
It includes traditional, tribal, and religious courts, and community-based systems – in resolving disputes.
Sub-factors:
9.1 Informal justice is timely and effective.
9.2 Informal justice is impartial and free of improper influence
9.3 Informal justice respects and protects fundamental rights
Importance/Necessity of Rule of Law
- To ensure accountability, equality and access to justice for all
- To strengthen international peace and security
- To promote holistic development of a society and nation
- To promote political stability
- To achieve economic and social progress and development.
- To encourage fairness and transparency
- To prevent the violation of human rights
- To discourage corruption
- To prevent the abuse of authority and power
- To establish a social contract between the government and people
Advantages of Rule of Law
- It promotes the freedom of judiciary
- It preserves the constitution
- It prevents arbitrariness and dictatorship
- It promotes fairness and ensures transparent, timely and predictable resolution of disputes
- It is easily accessible laws that create certainty and enforceability of legal rights
- It directly promotes higher economic growth
- It is correlated with improved health outcomes and greater peace.
- It provides quality services to the people
- Rule of law empowers the individuals and communities to use their justice mechanism
- Rule of law increases public trust in the legitimacy of the government
Challenges in Ensuring Rule of Law
- Limited access to justice, especially for vulnerable and marginalized populations
- Complexities of artificial intelligence and cybercrime
- Impeding law enforcement, fueling a breakdown in law and order by the political groups
- Ensuring decentralization of public offices and authority
- Ignorance and poverty
- Proliferation of hate speech and incitement to violence
- Climate change and the environment impacting on the security and livelihoods of people
- Need for independence and professionalism to serve as a check on abuse and a protector of rights and constitutional norms
- Excessive veneration of the law and legal procedures may be too costly.
- Overcrowding of public offices.
Limitations and Exceptions of the Rule of Law
1. Immunity:
- Immunity is special privilege given to certain individuals of certain authority which prevent them from lawsuit and prosecution as compared to the general population.
- It is an exception to the principle of rule of law.
2. Delegated legislation:
- It refers to the laws and orders promulgated by bodies other than parliaments.
- This is against the principle of rule of law.
3. Provision of special courts/administrative tribunals:
- There is provision of special court/administrative tribunal for certain public officials.
- This provision is differentiating the officials from the general population during legal procedures.
4. Emergency periods:
- Certain rights of a people and citizens are restricted during the state of emergency.
- Citizens may also be denied of some of their human rights and fundamental rights.
- This is an exception to the rule of law.
Ways to Promote Rule of Law
- Respect the system by each and everyone including leaders and public officials
- Discourage corruption and irregularities
- Ensure separation of power and authority
- Promote public awareness and advocacy campaigns
- Strengthen the role of mass media in ensuring rule of law
- Ensure political neutrality among the public servants/officials.
- Ensure the provision of citizen charter in the public offices
- Promote strict monitoring and supervision towards the action of public officials
- Provide proper guidance and training to promote rule of law
- Strengthen reward and punishment system
References and For More Information
https://www.un.org/ruleoflaw/what-is-the-rule-of-law/
https://worldjusticeproject.org/about-us/overview/what-rule-law
https://stoplearn.com/limitations-of-the-rule-of-law/
https://www.americanbar.org/groups/public_education/resources/rule-of-law/
https://assembly.coe.int/nw/xml/XRef/X2H-Xref-ViewHTML.asp?FileID=11593&lang=EN
https://www.britannica.com/topic/rule-of-law
https://blog.ipleaders.in/rule-law-relevance/#Introduction
https://www.unglobalcompact.org/what-is-gc/our-work/governance/rule-law
https://worldjusticeproject.org/our-work/research-and-data/wjp-rule-law-index-2021/factors-rule-law