
Table of Contents
What Do You Mean by Social Problems?
- Social problem is a social condition or behavior that a segment of society views as harmful to members of society and in need of remedy.
- Social problems are social conditions that disrupt or damage the society.
- A social problem has negative consequences for large numbers of people and that is generally recognized as a condition or behavior that needs to be addressed
- Thus in social problem there must be two things:
- An objective condition, like crime, poverty, communal tensions and so forth,
- The presence and magnitude of which can be observed, verified and measured by impartial social observers.
- There are various social problems like drug/substance abuse, child abuse, suicide etc.
- These social problems are briefly explained here.
Drug Abuse
Drug abuse, also known as substance abuse, is a patterned use of a drug in which the user consumes the substance in amounts or with methods which are harmful to oneself or others, and is a kind of substance-related disorder.
Drug abuse is one of the important social problems.
Most frequently abused drug/substance include:
- Alcohol
- Tobacco
- Marijuana
- Hashish
- Over-the-counter drugs like dextromethorphan and pseudoephedrine
- Benzodiazepines like Ativan and Valium
- Stimulants: methamphetamine or cocaine
- Club drugs: Ecstasy, ketamine, MDA, or Rohypnol
- Hallucinogens: LSD, mushrooms
- Inhalants: glue, lighter fluid, gasoline, paint thinner
- Narcotic painkillers: codeine and morphine
Signs and Symptoms of Drug Abuse
- Changed attitude in school/college/home
- Behavioral changes
- Change in the need for cash
- Change in self-care and appearance
- Change in level of energy
Consequences of Substance Abuse
- Academics: Declining grades, absenteeism, increased potential for dropping out of school
- Physical health:
- Injuries due to accidents such as car accidents
- Physical disabilities and diseases and the effects of possible overdoses
- Increased risk of death through suicide, homicide, accident and illness , diseases HIV/AIDS)
- Mental health
- Mental health problems such as depression, developmental lags, apathy, withdrawal
- Families:
- Family crises and family dysfunction can drain a family’s financial and emotional resources
- Social and economic consequences:
- Financial losses and distress
- Delinquency
- Other:
- Psychosocial dysfunctions
- Conduct problems
- Personality disorders
- Suicidal thoughts
- Attempted suicide and suicide
Prevention and Management Approaches of Drug Abuse
- Family prevention programs through enhancing family bonding, parenting skills and changing parental behaviors that may place a child at risk for later abuse. Example -multi-dimensional family therapy (MDFT)
- Community and school prevention programs by addressing risk factors for later substance abuse
Effective Treatment Approaches
- Medication and behavioral therapy, especially when combined that often begins with detoxification, followed by treatment and relapse prevention.
- Medications can be used to help reestablish normal brain function and to prevent relapse and diminish cravings
- Behavioral treatments is the most effective that engages patient in the treatment process to modify their attitudes and behaviors related to drug abuse and increase their healthy life skills
- Counseling/ Motivation
- Rehabilitation (Rehab center)
Other details of drug/substance abuse can be found here.
Child Abuse
- Child abuse is the physical or psychological/ emotional mistreatment of children by a parent or other caregiver that result in actual or potential harm to the child’s health, development or dignity.
- It is harm to, or neglect of a child by another person.
- It is a global social problem.
- According to World report on violence and health and the 1999 WHO Consultation on Child Abuse Prevention, there are four (4) types of abuse that can happen to a child. They are:
- Physical Abuse
- Sexual Abuse
- Psychological abuse
- Neglect
- One of three girls and one in five boys are sexually abused by an adult at some time during childhood.
- Most abusers are a parent or someone in the family or someone the child knows (80%).
- Families with more than 4 children have higher rates of abuse and neglect, especially if their living conditions are crowded or they live in isolated areas.
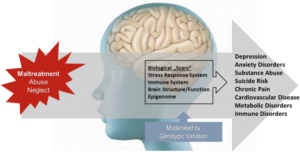
Effects/ Consequences of Child Abuse
- Long term physical problems including physical disability
- Sexual and reproductive
- Sexual dysfunction
- STDs/HIV/AIDS
- Unwanted pregnancy
- Teenage pregnancy
- Psychological behavioral
- Depression and anxiety
- Alcohol and drug abuse
- Poor school performance
- Suicidal behavior
Suicide
- It is the intentional way of hurting oneself resulting in death
- Many factors are associated with suicide that increase the risk of it
- It is a social problem as it’s risk in a population increases when the social context fails to provide a healthy sense of purpose and belonging, contributing to an individual’s sense of contribution and connection
- Suicide can be prevented as it has protective factors as :
- Coping and problem-solving skills
- Cultural and religious beliefs that discourage suicide
- Relationship with friends, family, and community support
- Supportive relationships with care providers
- Availability of physical and mental health care
Conflicting Situation
- Strong disapproval between people, groups, etc., that results in often angry argument
- Conflict can happen when family members have different views or beliefs that clash.
Causes of Conflict
Changes in the family situation can also take a toll on the family and contribute to conflict. This may include events such as:
- Separation or divorce
- Moving to a new house or country
- Change in financial circumstances.
- Parent can also change their opinions, values and needs and they may find they are no longer compatible
Consequences of Conflict
- Human right violation
- Direct violence
- Displacement
- Sexual cruelties
- Increased exposure to HIV/AIDs
- Physical abuse
- Psychological impact
- Culture of violence
Conflict Management Strategies
- Accommodating
- Avoiding
- Collaborating
- Compromising
- Competing
References and For More Information
https://www.cdc.gov/suicide/facts/index.html
https://medlineplus.gov/druguseandaddiction.html
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/child-abuse/symptoms-causes/syc-20370864
https://www.unicef.org/nepal/topics/child-abuse
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2205428/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18626465/
https://www.igi-global.com/dictionary/conflict-situation/50863