Table of Contents
What is Ergonomics?
- Derived from the Greek words ‘Ergon’ meaning work and ‘nomos’ meaning laws.
- Thus, ergonomics can be simply defined as the how workplace and equipment can be best used and designed for comfort, safety, efficiency and productivity.
- “Ergonomics (or human factors) is the scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of the interactions among human and other elements of a system, and the profession that applies theory, principles, data and methods to design in order to optimize human well-being and overall system performance.”-International Ergonomics Association Executive Council, August 2000
- Simply, ergonomics is the branch of science that deals with the people and their working environment.
- Ergonomics is for worker safety and health and maintaining the healthy working environment.
- It can also be understood as the study of worker in their working environment.
- Ergonomics is concerned with designing or arranging workplaces, products and systems so that they fit the people who use them and the maximum output can be obtained from them
- Ergonomics extends beyond the proper posture of the workers.
Importance of ergonomics:
a) Increases productivity
- Best ergonomic solution enhances the productivity
- Ergonomic reduces the unwanted tension, awkward position of the body.
- Ergonomic is focused in making the work your easier and comfortable, this thereby reduces any kind of stress, risk and enhances the satisfaction and productivity.
b) Reduces the cost
- Ergonomics can be considered as the one-time investment
- As ergonomics is focused about marinating the better health of the worker it can further reduce the cost of compensation that would be made by the injured or unhealthy staffs.
- It also reduces the indirect and the opportunity cost that could have incurred due to injury.
c) Improves the quality of the work
- Improved ergonomics favors the favorable environment where the workers can work efficiently.
- As the ergonomics improves, level of satisfaction in the quality of the work increases.
d) Others
- Helps to reduce the absenteeism due to more comfort, safety and healthy working environment
- Assurance to the worker as their workplace is safer (acts as the motivation)
- More focus on the working environment and worker’s health makes them feel valued and boost of moral.
Principles of Ergonomics
There are 10 fundamental principles of ergonomics which are:
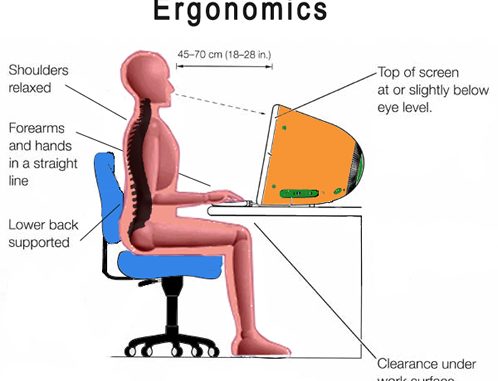
1. Work in neutral postures
- Proper posture maintenance is necessary
- Working too long with “C” curve can cause strain
- Keeping the proper alignment of neck hands wrist are also necessary
2. Reduce excessive force
- Excessive pressure or force at the joints can cause injury
- Better to minimize the work that requires more physical labor
3. Keep everything in reach
- Keeping everything in reach would help in avoiding unneeded stretching and strain
- More or less this principle is related with maintaining good posture.
4. Work at proper height
- Working at right makes things way easier
- Sometimes height can be maintained by adding extensions or avoiding extensions on the chair or tables
5. Reduce excessive motions
- Repetitive motion needs to be avoided
- This can cause disorder and numbness in long run
- Motion scan be reduced by the use of power tools
6. Minimize fatigue and static load
- Fatigue is common in strenuous work
- Having to hold things for longer period is example of static load
- Fatigue can be reduced by the intervals and the breaks between the works.
7. Minimize pressure points
- One needs to be aware of pressure points
- Almost everyone of has to sit on chairs that had cushioning, one of the pressure point is behind knees, which happens if air is too high or when you dangle your legs. Pressure point is also created in between your thigh and the bottom of a table when you sit.
- Anti-fatigue mats or insole can be used
8. Provide clearance
- Work area should have enough clearance
- Let the worker not worry about the bumps that they have to encounter on daily basis.
9. Move, exercise and stretch
- Move and stretch when you can
- It better to take intervals between the works and stretch and move along
- Stretching technique may differ and depend on the work one does
10. Maintain a comfortable environment
- This principle is focused on the other component of the working environment.
- It is concerned about the lightening, space, cool air and many more.
Ergonomic Injuries/Musculoskeletal Disorder (MSDs):
- Ergonomic injuries or MSDs can affect the muscles, nerves, tendons, ligaments, joints, cartilage and spinal discs.
- Musculoskeletal disorder (MSDs) is also known as the repetitive motion injury.
- MSDs are the condition that can affect muscles, joints and bones.
- MSD are caused due to individual risk factor or ergonomic risk factor.
- MSDs are the single largest category of workplace injuries and are responsible for almost 30% of all worker’s compensation costs
- Individual risk factor include age, nutrition, activity, etc., while ergonomic risk factors includes:
- High task repetition
- Awkward body posture for longer period
- Sitting in same posture
- Lifting heavy weights.
However, MSDs can be simply prevented as:
- Avoiding repetitive action.
- Use of machines for strenuous action.
- Maintaining the body posture.
- Use of cushion pads, lumbar support whiling sitting for the longer time.
References and for more information:
https://ehs.unc.edu/workplace-safety/ergonomics/
https://www.posturite.co.uk/help-advice/learning-resources/what-is-ergonomics
https://www.ergonomics.org.uk/Public/Resources/What_is_Ergonomics_.aspx
https://www.ergonomics.com.au/what-is-ergonomics/
https://www.hsa.ie/eng/Publications_and_Forms/Publications/Occupational_Health/Ergonomics.pdf
https://osha.oregon.gov/OSHAPubs/ergo/ergoadvantages.pdf
https://ergo-plus.com/workplace-ergonomics-benefits/
https://www.nibusinessinfo.co.uk/content/importance-ergonomics
https://www.uncagedergonomics.com/blog/principles-of-ergonomics-in-the-workplace/
https://mn.gov/bms-stat/assets/cd_ergo_priciples.pdf
https://www.danmacleod.com/ErgoForYou/10_principles_of_ergonomics.htm
https://ergo-plus.com/fundamental-ergonomic-principles/
https://ergo-plus.com/musculoskeletal-disorders-msd/
https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/ergonomics/default.html
https://www.healthline.com/health/musculoskeletal-disorders#causes