Table of Contents
What is Hypertension?
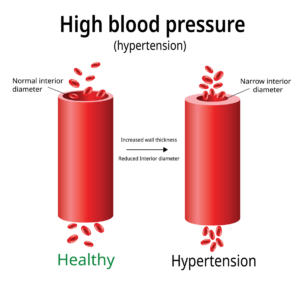
- When the force or pressure of the blood pushing against blood vessel walls becomes excessively high, it is known as hypertension of high blood pressure.
- Hypertension (HTN) refers to the increased pressure of the blood against the blood vessel walls of the body.
- Hypertension (HTN) is also commonly known as ‘high blood pressure’
- Clinically, systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure of ≤ 90 mmHg are considered as having ‘hypertension’.
- The reading of blood pressure has two numbers; systolic and diastolic.
- Systolic blood pressure, which appears as the top number, measures the force exerted on the blood vessel walls when your heart beats or contracts.
- Diastolic blood pressure, which appears as the bottom number, measures the force exerted on your blood vessels between heartbeats while relaxing
- Systolic and diastolic blood pressure should be less than 120 and 80 mmHg, respectively, to be considered normal.
Key Facts
- Hypertension is serious medical condition that greatly raises the risk of developing heart, brain, kidney, and other problems
- Worldwide, 1.28 billion people between the ages of 30 and 79 are estimated to have HTN, with the majority (two-thirds) residing in low- and middle-income nations
- Adults with hypertension are reportedly 46% less likely to be aware of their condition.
- Adults with HTN are only diagnosed and treated in 42% of cases.
- Approximately one in every five persons (21%) has HTN under control.
- Hypertension is a major contributor to premature death all around the world
- Reduce the prevalence of HTN by 33% between 2010 and 2030, one of the worldwide goals for non-communicable diseases
Risk Factors
- Having blood relatives who suffer from diabetes, heart disease, or high blood pressure
- Age above 55 years
- Being overweight
- Don’t have enough physical exercise
- Consume sodium-rich meals (salt)
- Use tobacco or smoke a cigarette
- Are a regular alcoholic
Causes of Hypertension
- Oftentimes, the root cause of hypertension is unknown. It frequently stems from an underlying condition.
- High blood pressure which does not occur due to another condition or disease is known as primary or essential hypertension.
- If any underlying condition is a cause of increased blood pressure, then it is called as secondary hypertension
- Primary HTN can result from multiple risk factors mentioned above in risk factors
- Conditions that can lead to such HTN include:
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Diabetes, resulting from kidney problems and nerve damage
- Peochromocytoma, a rare cancer of an adrenal gland
- Cushing’s syndrome
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Pregnancy
- Sleep apnea
- Obesity
Symptoms of Hypertension
- Dizziness
- Chest pain
- Palpitations
- Irregular heartbeat
- Headache
- Vomiting and/or nausea
- Shortness of breath
- Blurry vision
- Nose bleeding
- Blood in the urine
- Fatigue
Blood Pressure Ranges
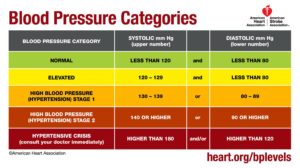
According to the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults (2017 Guideline), blood pressure levels is categorized as follows:
| Range | Systolic | Diastolic |
| Normal | Less than 120 mm Hg | Less than 80 mm Hg |
| Elevated | 120–129 mm Hg | Less than 80 mm Hg |
| High blood pressure
(hypertension) |
130 mm Hg or higher | 80 mm Hg or higher |
Likewise, according to the American Heart Association, the category of blood pressure are:
Consequences/complications of Uncontrolled Hypertension
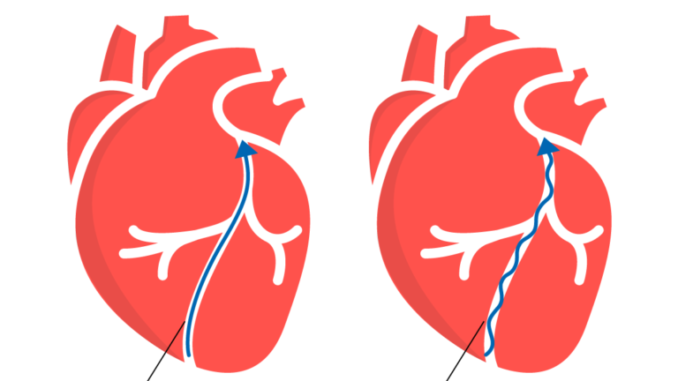
- Uncontrolled hypertension can cause complications through atherosclerosis.
- Atherosclerosis is when plaque develops on the walls of blood vessels, causing them to narrow.
- This narrowing makes HTN worse, as the heart must pump harder to circulate the blood.
- This can lead to:
- Severe chest pain
- Heart failure and heart attacks
- Aneurysm
- Kidney failure
- Stroke
- Hypertensive retinopathies that can lead to blindness
Preventive Measures

- Limiting salt consumption (to less than 5g daily).
- Eating more fruit and vegetables.
- Having regular physical activity, at least 150 minutes of physical activity each week (about 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week)
- Avoiding use of tobacco.
- Reducing alcohol consumption.
- Reducing the intake of foods that have high saturated fats
- Eliminating/reducing trans fats in diet.
Management of Hypertension
- Reducing and managing stress.
- Regularly checking blood pressure.
- Treating high blood pressure.
- Managing other medical conditions.
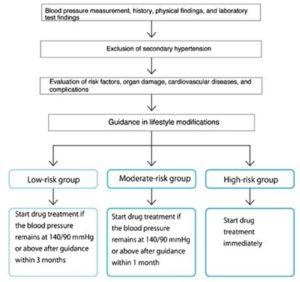
Treatment
Medications for HTN include:
- diuretics, including thiazides, chlorthalidone, and indapamide
- beta-blockers and alpha-blockers
- calcium-channel blockers
- central agonists
- peripheral adrenergic inhibitor
- vasodilators
- angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
- angiotensin receptor blockers
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/hr20083
WHO Response on Hypertension
- The World Health Organization (WHO) is aiding nations in to lower HTN as a public health issue
- A new WHO recommendation on the pharmaceutical management of adult HTN was published in 2021
- This offers evidence-based suggestions for starting hypertension therapy as well as suggested follow-up intervals
- In September 2016, WHO and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) established the Global Hearts Initiative, which includes the HEARTS technical package, to assist countries in increasing the prevention and control of cardiovascular disease.
- The HEARTS technical package’s six modules, which include “Healthy-lifestyle counseling,” “Evidence-based treatment protocols,” “Access to essential medicines and technology,” “Risk-based management,” “Team-based care,” and “Systems for monitoring,” offer a comprehensive plan for enhancing cardiovascular health in all nations
- In September 2017, WHO collaborated with Resolve to Save Lives, a Vital Strategies project, to assist national governments in implementing the Global Hearts Initiative.
- In 18 low- and middle-income countries since the program’s launch in 2017, 3 million patients have received protocol-based hypertension therapy using person-centered models of care.
References and For More Information
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension
https://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/about.htm#:~:text=High%20blood%20pressure%2C%20also%20called,blood%20pressure%20(or%20hypertension)
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/symptoms-causes/syc-20373410
https://www.webmd.com/hypertension-high-blood-pressure/guide/blood-pressure-causes
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/high-blood-pressure/symptoms
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/150109#diet
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/high-blood-pressure-hypertension/treatment/
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4314-hypertension-high-blood-pressure
https://www.healthline.com/health/high-blood-pressure-hypertension#treatment
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5733954/