
Table of Contents
What is Vitamin B?
- The term “vitamin B” refers to not one, but a group of eight water-soluble vitamins that are necessary for various metabolic functions
- Vitamin B complex is another name for vitamin B
- The names of eight types of vitamin B are:
-
- B1 (Thiamine)
- B2 (Riboflavin)
- B3 (Niacin)
- B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
- B6 (Pyridoxine)
- B7 (Biotin)
- B9 (Folic Acid)
- B12 (Cobalamin)
- Vitamin B is widely available in both plant and animal dietary sources and cannot be stored by the body, must be replenished daily
- In general, vegetarian food has less vitamin B than non-vegetarian food. Hence, Vitamin B supplements are highly beneficial for vegetarians.
Sources of Vitamin B
- Whole Grains (Brown rice, Barley, Millet)
- Meat (Red meat, Poultry, Fish)
- Eggs And Dairy Products (Milk, Cheese)
- Legumes (Beans, Lentils)
- Seeds And Nuts (Sunflower seeds, Almonds)
- Dark, Leafy Vegetables (Broccoli, Spinach)
- Fruits (Citrus Fruits, Avocados, Bananas)

Functions
- Vitamins B1 and B2 aid in the synthesis of energy as well as enzymes that affects the heart, neurons, and muscles
- Vitamin B3 helps in the production of energy that our cells require to sustain healthy skin, digestion, and nervous system function
- Both vitamins B5 and B12 are necessary for healthy growth and development. B12 also supports the nervous system and the production of red blood cells, and helps the body use other vitamins B and carbohydrates
- Vitamin B6 helps the brain and immunological systems as well as the formation of blood cells. It also interacts with other vitamins to help break down protein
- Vitamin B7 assists the body in production hormones and helps in the breakdown of protein and carbohydrates
- When present in diet, vitamin B9 helps to produce blood cells and is essential for the synthesis and maintenance of DNA. Due to which, it becomes a very important vitamin during pregnancy for ‘fetus’ development.
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of Vitamin B varies with the age. The daily recommended dietary amount of Vitamin B according to the age groups is:
- Infants (adequate intake) (0 – 6 months) – 0.4 micrograms per day (mcg/day)
- Child (7 – 12 months) – 0.5 mcg/day
- Child (1 – 3 years) – 0.9 mcg/day
- Child (4 – 8 years) – 1.2 mcg/day
- Child (9 – 13 years) – 1.8 mcg/day
- Males and females age 14 and older – 2.4 mcg/day
- Pregnant teens and women – 2.6 mcg/day
- Breastfeeding teens and women – 2.8 mcg/day
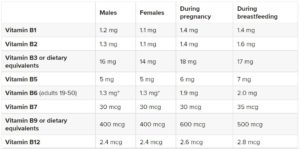
Likewise according to National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements, the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for each of the B vitamins is given below:
Health Benefits of Vitamin B
Vitamin B helps to prevent infections and also promote and support:
- Cell growth
- Growth of RBC
- Brain function
- Eyesight
- Digestion and appetite
- Proper nerve function
- Hormones and cholesterol production
- Cardiovascular health
- Muscle tone and energy levels

Likewise, other health benefits of Vitamin B are:
- It helps to heal the wounds faster
- Helps to treat anxiety
- Improves overall body performance
- Helps to treat osteoporosis
- Helps in eliminating ADHD symptom
- Cures stomach problems
- Helps in premenstrual syndrome
- Solves the problem of canker sores
Source: https://www.lybrate.com/topic/vitamin-b-benefits-sources-and-side-effects
Symptoms of Vitamin B Deficiency
There are various symptoms of Vitamin B deficiency. Some of the major symptoms are:
- Skin rashes
- Cracks around the mouth
- Scaly skin on the lips
- Swollen tongue
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Anemia
- Confusion
- Irritability or depression
- Nausea
- Abdominal cramps
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Numbness or tingling in the feet and hands
- Mental problems like depression, memory loss, or behavioral changes
Groups At High Risk of Vitamin B Deficiency
- Older adults, pregnant mothers and people with certain health condition are the groups that are particularly in high risk to vitamin B deficiency. They require more of some vitamin B subtypes than others
- Certain condition like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, HIV, and alcohol use disorder, can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb vitamin B, increasing the risk of deficiency
- Vegans and strict vegetarians are usually at risk of developing a B12 deficiency as this vitamin is only found in animal source
- People under certain medications are also in the risk of Vitamin B deficiency. Certain medication can decrease the absorption or levels of vitamin B
Consequences of Deficiency
Deficiency in various forms of Vitamin B can result in the development of following diseases:
| Types of Vitamin B | Deficiencies |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) | Beri-Beri
Wernickes Koasoff Psychosis |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | Ariboflavinosis |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | Pellagra |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | Burning feet syndrome |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) | Anemia |
| Vitamin B7 (Biotin) | Dermatitis
Enteritis |
| Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid) | Megaloblastic anemia
Neural tube defect |
| Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Megaloblastic anemia |
- Vitamin B are beneficial to health and necessary for the body’s overall operation, but supplementing with them can have certain risks, especially when taken in large amounts (overdose)
- Despite the fact that B complex has been found to aid in the prevention of a number of malignancies, there is data suggesting that it may raise the risk of lung cancer in males who smoke.
- High dosages of B6 can result in severe skin sores, light sensitivity, and nerve damage.
- Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, in large dosages can cause liver damage, high blood sugar, skin flushing, and vomiting
- B-complex supplements also have the potential to make your urine quite yellow. Although it is not dangerous
Prevention of Vitamin B Deficiency
- Vitamin B deficiency can be prevented by consuming food and drinks rich in Vitamin B.
- Eat a complete diet of:
- Meat
- Grains
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- In cases where a person cannot eat meat, eggs or dairy product, he/she should get Vitamin B12 from fortified foods.
- Additionally, various supplements can also help to prevent and treat Vitamin B deficiency. However, supplements should be taken after consultation with the medical person/doctor.
- Avoiding alcohol: Frequent alcohol consumption can damage the digestive system and makes it difficult for the body to absorb Vitamin B.
References and For More Information
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-b-complex#side-effects
https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/vitamin-b-complex#benefits
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-b-complex#benefits
https://www.healthline.com/health/symptoms-of-vitamin-b-deficiency#vitamins-b-1-and-b-2
https://www.everydayhealth.com/pictures/surprising-health-benefits-b-vitamins/
https://www.healthxchange.sg/food-nutrition/food-tips/vitamin-b-best-food-sources-signs-deficienc
https://www.lovetoknowhealth.com/diet-and-nutrition/facts-about-vitamin-b
https://www.medbroadcast.com/channel/nutrition/supplements-and-nutraceuticals/b-vitamin-complex-quick-facts
https://www.lybrate.com/topic/vitamin-b-benefits-sources-and-side-effects
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/vitamin-b
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamins-and-minerals/vitamin-b/
https://www.healthline.com/health/symptoms-of-vitamin-b-deficiency#vitamin-b-3
https://medlineplus.gov/bvitamins.html
https://www.godigit.com/health-insurance/nutrition/vitamin-b-deficiency